Let’s face it. Social media, like digital marketing initially, has been overhyped. We don’t even need any more “social media” gurus in 2011. We just need executives and marketers who understand the channel well enough to be realistic, patient and smart. We’ve been asking “what?” and “why?” for several years now, and the big questions for 2011 are “who?” and “how?”
It’s time to get back to the basics this year, and recognize that when a CEO or marketer says “I want a popular Facebook or YouTube account,” what she probably means is this:
She wants to increase sales by: a) making her company appear contemporary, b) capitalizing on a new and efficient way to market, and c) engaging more meaningfully with her customers than is possible through advertising. But the operative word in that last sentence is “grow,” because the rest is a means to an end. Even if she’s using a very soft, educational and entertaining approach to social media, her goal is to sell. Her goal is to sell. And that’s okay.
Consider for a moment the evolution of advertising and marketing agencies (dates/credit to Big Fuel, the creators of the embedded video:
- Advertising Agency: The first traditional advertising agencies were established in the 1850s to help brands drive awareness through newspapers, then later radio and television. They distinguished many otherwise undifferentiated products, and taught the business community that the medium works.
- Direct Marketing Firm: In the 1960s through 1980s we saw direct marketing proliferate. DM or DR (direct response) agencies focused less on driving awareness, and more on generating measurable sales through accountable channels like telemarketing, direct-response mail and catalogs.
- Digital Agencies: From 1993 to 1999, we saw the emergence of digital agencies helping optimize the emergence of the Internet. It was the ultimate direct-response playground, a place to conduct more targeted advertising, and most importantly… an efficient way to target buyers while they were looking (searching), then engage them in custom ways that were cost-prohibitive before.
- Stagnation: After the bubble burst, and before web 2.0 became vogue, consumers began to protect themselves from ads through spam filters, ad blockers and simply ignoring what they could. Forced homepage takeovers and prerolls, while breaking through ad fatigue, has brought back the corporate desperation of dinner-time telemarketers and junk mail.
- Social Media Experts: Now we’ve got thousands of people claiming to be “social media marketing” experts, and that annoys me as a former Product Director. I want someone who understands my product, category and customers above all… and I hope they’ll come with some common sense and experience about the workings of social media. But a channel-specific “guru” can be very difficult to weave into a brand team.
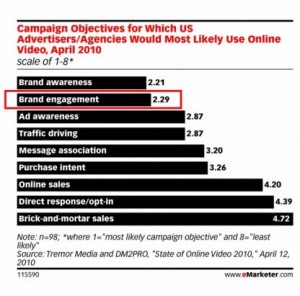
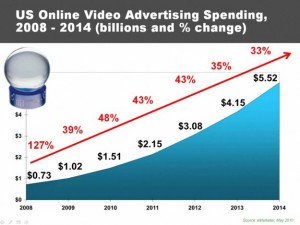
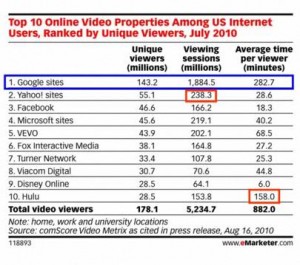
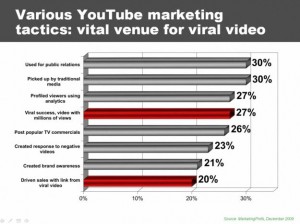
Meanwhile, where does online-video marketing fit in? It has been sometimes dangerously isolated from social media, which is odd to me. Even more tragically, online-video has been buried in the “black hole” of digital media advertising. I hope a marketer can appreciate that oline-video marketing is a broader discipline than simply buying display ads (pre-rolls) or “going viral.” So where does online-video and social-media belong? And why are so few brands achieving their social media and/or online-video marketing goals?
First, some goals are unrealistic (going “viral”). More commonly, however, brands are “pushing too hard,” by trying to marry prospects before a proper courtship. Although less common, some brands have fallen to the opposite extreme. Soft, charitable education and entertainment comes at the expense of any meaningful business return.
The balance (being a “social” company or brand but also selling products or services) is difficult, hence the explosion of social-media experts that understand the medium and how marketing can play nicely. This balancing act impacts online-video as much as any other component of online-marketing or social media. Is a video designed to capture the hearts, minds, and wallets of the largest possible audience? Or is it built to capture the attention of prospects, and propel them from awareness to sale (and even loyalty and advocacy)?
The answer, of course, is yes. Video can and should do all of those things. Although that requires a strategy, and different video content for various stages of the “funnel.”
This video below (an oldie but goodie) speaks to the need of a “customer engagement” (CE) agency or specialist, and I would contend that the CE term is more fitting than social media. Customer engagement what companies want and need, and online video (as well as social media) is a way to do it. Companies don’t need a “social media” guru, they simply need marketers and agencies who know what’s appropriate for these mediums and how to tap them efficiently and effectively.
Again, social media is just another place to market with some new and unique nuances. It’s certainly different from traditional “reach and frequency” media or the “hyper targeting” Internet as we’ve known it. While social-media marketing can complement those other forms of advertising, it’s risky to bring best-in-class advertising approaches to social media without refining them.
The bottom line is that we can be “social” and savvy about online video… without adding a lick of value to customers or the business. We can also add tremendous customer and business value without being so damned social or “viral.” So what’s the answer?
- First, let’s remember what we’re really trying to do. We want to use social media to achieve justifiable goals: target, find, help, educate, court, convince and engage new customers.
- This means we’re creating a social-media presence not just to “hang out and be cool” or go “wicked viral,” but to add value to both customers/prospects and our company/brand.
- A lot of social media and online-video fits nicely into a public relations agency, even if most of them are more familiar with media influence than customers. And it’s everyone’s job not a guru, specialty agency or department (for instance, even the traditional media buyer needs to know social so they don’t turd drop in a medium where people are far less interested in “boast and push” advertising).
- If we’re offering a really good product or service, customers will voluntarily use social media to help others find us. We can encourage that, but ultimately it’s something they’ll do to reward us, not just because we ask them to “like” on Facebook or “subscribe” to our YouTube channel.
- Finally, there are a lot of things best-in-class “social” brands are NOT doing. They aren’t simply trying to become “popular” via social media or “viral” on YouTube. And they’re certainly avoiding the temptation to become a content creator or publisher unless it’s a necessary “means to an end.” Entertainment is not job of a brand, can’t be done well by most sales/marketing teams, and can severely detract a team from great marketing strategy and execution.
- Great brands aren’t pimping themselves on social media. They’re trying to earn the right to introduce products or services appropriately.
I’ll get off my soap box now, and let you enjoy this animation. If you’re not careful, it might just give you ideas on how to attack the two big 2011 questions: “who” and “how.”