YouTube Changes: Phases, Winners, Losers & Gremlins
While preparing for an article for ReelSEO, I happened to be watching Gremlins (1984). I couldn’t help but see the parallels between YouTube changes and the cute and fuzzy Mogwai’s mutating into the entertaining but deadly Gremlins (pictured here). We’re about to see YouTube go “pro” in an extreme form, and that’s one of the biggest changes the video-sharing site has made in its history.
Don’t get me wrong. I like change. Even if it involves some interim puss-oozing pods during the “pupil” stage. And while I mourn for my RIP and decaying fellow independent creators (and my own channel), I am excited to see how YouTube/Google becomes a cable network despite the significant battles by studios, networks and serious content producers. It’s inevitable progress… even though I’ll miss the community (but they’re there somewhere, right?).
This post will be somewhat jumbled since my thoughts for the ReelSEO piece are still sorting themselves out. I would also value some input from people who’ve been watching YouTube’s transitions even more closely than me.
Some facts & phases of YouTube’s evolution (with considerable help from Urgo6667‘s ugly but robust SocialBlade data repository)
- Phase 1: YouTube in the 2009-2010 placed considerable emphasis on an exclusive and select pool of YouTube Partners. These independent content creators were rewarded with preferred placement throughout the site (driving views), advanced channel features, and premium monetization (sharing the income from higher yield advertisements from brands that feared consumer-generated content).
- Phase 2: Just as some governments reportedly destabilize other countries by introducing currency, the income caused new behaviors. As Archfiend laments in this video, the advertising income helped fuel desperate habits like faking thumbnail images, begging for comments and asking for 5 stars or thumbs up.
- Phase 3: YouTube, once the home of free speech and cat videos, began to become increasingly commercial. Once subtle ads soon blanketed the homepage. Optional prerolls became mandatory. The lines blurred between popular content and what was “featured” (based on advertising dollars or preferential content placement for select creators).
- Phase 4: Some prolific YouTube pioneers left the site jaded. These include Renetto, Pipistrello, and Comedian SeanBedlam (see his frustrated video posted in August announcing he’s quitting).
- Phase 5: As a great magician distracts you from his slight of hand, YouTube introduced the NextUp program. It gave $35K checks to a new crop of YouTube Partners to fuel their content.
- Phase 6: Now YouTube is going after cable and investing $100 million in professional content
But as 2011 progressed, YouTube changes resulted in views spread out in cryptic ways. Some YouTube channels have taken significant hits from these changes in which videos appear in powerful areas such as search results, “related videos” and “spotlights.”
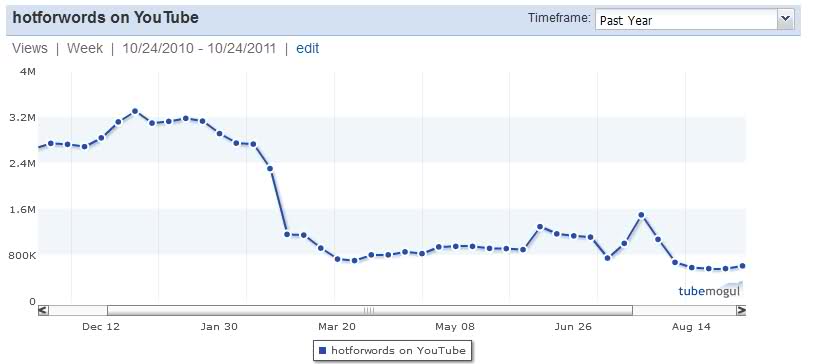
I’ve shared my own sharp decline since September (in October I averaged 64% fewer views then 3 months ago), but this chart from once-popular HotForWords tells a typical story…
Fall of Pioneers… The decline of solo creators is not unlike the fate of Indie singers online… as viewers shifted to mainstream content that arrived late to the party. But check out some non-trivial examples:
- TheStation, which was launched by top YouTubers, went from more than 272,000 views October 2010 to under 110,000 in October 2011.
- Smosh, one of the most subscribed channels, is down 94% last month relative to 6 and 3 months ago. They were once the darlings of YouTube with frequent sponsors.
- SMPFilms, an early pioneer of YouTube meetups, is down 56% from 6 months ago… getting about 63,000 views currently (the drop is almost identical to the decline of Google’s channel on YouTube). MysteryGuitarMan (MGM) took a similar hit, and so did MediocreFilms.
- Some (but a minority) of the decline could be the creator’s diminished productivity. For instance I posted less frequently. But this seems unlikely given that MGM and Smosh are still rolling out new videos that get significant views.
- The decline is, perhaps, simply a return to normal. Most Partners saw a dramatic “artificial” lift in monthly views that were not dependent on their new content. In effect YouTube throttled creators and then stopped.
- More than 50% of my own views comes from related videos. Some of that might be based on an algorithm that attaches similar videos, and that’s presumably less likely to change. But YouTube may continue to “throttle” my videos as related videos, meaning I’ve got further room to drop. Here’s hoping the Wizards of Al don’t decide to beat me down again for this post.
- YouTube has not seen a decline in viewers, so the views are being spread out to the new “mini Partners” and other creators.
- Here are some of the fastest-growing Channels according to SocialBlade analysis: Vevo (which took a 1900% growth relative to 3 months ago), HollywoodTV, StanfordUniversity, and PlayStation with a remarkable 500K views a month.
- Stay tuned… working with Urgo I might publish a list of the biggest losers/gainers.
Thoughts? Observations? Insights? Bring ’em. And thanks mystery man (you know who you are).