I was invited to join a web studio yesterday that provides a fixed CPM or cost per 1,000 views. That means the network promises you’ll earn no more and no less per video view… many of my friends have made that choice. It forced me to examine my current CPM and consider how that might change. Is it in my interest to accept a “floor/ceiling” amount? Or am I optimistic it will grow, and eager to benefit from that?
So today let’s look at attic rats, income for online-video ads, and contrast the sorry current state with what industry analysts predict.
Jim Louderback, CEO of Revision3, recently posted an intriguing article/rant about CPM prices… it’s titled “How Rats in the Attic Made Me Realize What’s Wrong With Prerolls.” Let’s examine the highlights to get a sense about why brands and online agencies have artificially depressed online-video advertising (despite shifts from print/TV to this medium).

Problem (according to Louderback):
Unfortunately, even though those two video ad experiences are as different as rats and wine (KN note: Louderback was inspired having received junk mail for rat extermination and wine), they were probably priced at similar CPMs. That’s because the online video ad market – particularly the pre-roll market — hasn’t progressed nearly as far as print. Those were two markedly different experiences, with wildly different levels of engagement. However, for many buyers, agencies and brands an on-line video pre-roll is valued the same wherever it runs, regardless of viewer intent, ad placement and playback environment. It’s as if Trump and “Take Air USA” paid exactly the same for those two print placements – even though their impact is worlds apart.
Solution (according to Louderback):
If you’re a video ad buyer, understand the value differences between in-banner impressions and engaged in-stream video ads. Focus your energy on the latter, and you’ll get far better results than if you lump the two together. Even though engaged, in-stream video ads will be more expensive, they are still a great bargain – especially if when you target demographic or content affinity along with the in-stream purchase.
Now let’s pull a “you show me yours I’ll show you mine” to see what poor targeting has done to the online-video economy.
Here’s a question for those brave enough to admit in comments below (feel free to use an anonymous name). What’s your YouTube CPM (income per 1000 impressions)? In other words, how much do you make per 1,000 views? It’s easy to compute: simply take your earnings in a given month, divided by the total number of views you get per month (divided by 1,000).
- Example: you earned $200 last month. Your videos were viewed 100,000 times. So you divide $200 by (100,000/1,000). You get $200 divided by 100 equals $2.00 CPM.
- Since YouTube keeps about a half, that would mean the company is fetching about $4 CPM… which is horrendously low if prerolls were used.
- Show us your CPM?
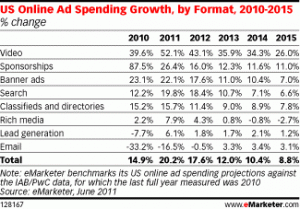
Good news: eMarketer puts online-video advertising growth at more than 43% in the next year and 35% the next year. As marketers become more targeted and sophisticated, we should easily see a CPM lift of 20-30%.